P0103 Code (Symptoms, Causes, and How to Fix)
Modern engine controls rely on input from sensors like the mass airflow (MAF) sensor, measuring air volume. Code P0103 indicates a fault in the mass airflow circuit. This interrupts the data stream to engine computers, hampering performance and economy.
This article looks at the potential causes of a P0103 code, its severity, and how to properly troubleshoot and fix this trouble code.
What Does Code P0103 Mean?
Diagnostic trouble code P0103 is indicative of an issue within an engine’s mass air flow circuit. More precisely, a vehicle’s PCM/ECM has determined that the voltage reflected by this circuit exceeds that which is expected. However, to fully understand the gravity of DTC P0103, one must first familiarize themselves with the function of an engine’s MAF sensor.
A vehicle’s MAF sensor is located within the engine’s intake tract, usually directly downstream of the air filter housing itself. This sensor samples all incoming airflow, thereby rationalizing airflow volume as a whole. This information is then relayed to a vehicle’s operating software.
Feedback provided by a vehicle’s MAF sensor is used to formulate a number of essential equations, including those that determine an engine’s relative fuel trims. Without feedback of this type, combustion efficiency suffers.
In the case of DTC P0103, an engine’s PCM/ECM has determined that feedback provided by the MAF sensor is skewed to the high-end of the anticipated range, thereby proving irrational. Simply put, an engine’s operating software has determined that this data is outside the bounds of that which is logical in nature.
Related: Code P0068, Code P0100, Code P0101, Code P0102
Symptoms of Code P0103

Diagnostic trouble code P0103 is often accompanied by a number of additional symptoms, some of which tend to be more serious than others. Recognizing each of these symptoms can prove valuable when attempting to diagnose and remedy the issue at hand.
The following are several of the most common symptoms associated with DTC P0103.
- Check engine light
- Erratic engine idle
- Difficulty starting
- Stalling at idle
- Dark-colored or heavy exhaust
Causes of Code P0103
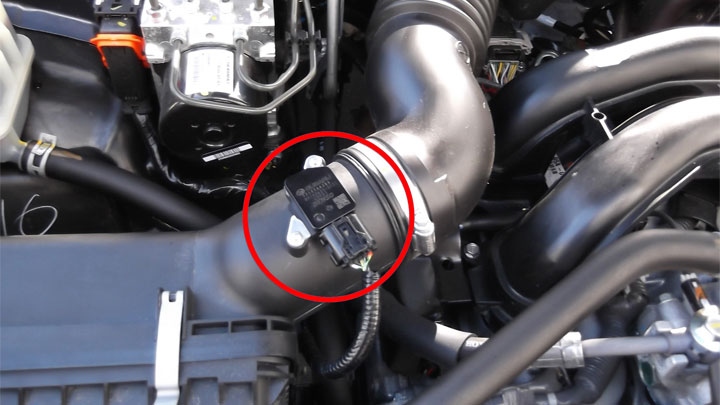

Diagnostic trouble code P0103 can be caused by a host of underlying issues, each of which is distinct in nature. Understanding these possible causes is often the difference between getting your vehicle back on the road in an expedited fashion and utter bewilderment.
The following are several of the most common causes of DTC P0103.
- Dirty MAF sensor
- Faulty MAF sensor
- Circuit interference
- Severe intake leak
- Compromised MAF circuit wiring
- Faulty PCM/ECM
Is Code P0103 Serious?
In general, diagnostic trouble code P0103 is considered to be quite serious in nature. This stems from the fact that code P0103 is often accompanied by a number of rather impactful drivability-related symptoms.
These symptoms include issues with engine stalling, and difficulty starting. This presents a very real possibility of becoming stranded along the roadside.
Additionally, any vehicle plagued by a P0103 diagnostic trouble code is unlikely to pass emissions testing, in any state where such testing is mandated by the government. This, in itself, can cause its own share of hardship for any motorist.
In any event, the root cause of diagnostic trouble code P0103 should be thoroughly diagnosed and remedied as soon as possible. Doing so prevents any further complications, and greatly reduces the chance of being stranded without additional resources.
How to Fix Code P0103

The following steps can be used to assist in diagnosing and repairing the root cause of your vehicle’s P0103 diagnostic trouble code. As always, be sure to consult factory specific service literature for your particular vehicle before attempting any such repairs.
#1 – Check For Additional DTCs
Before beginning the diagnostic process, check for the presence of any additional diagnostic fault codes. Any such codes should be thoroughly diagnosed before proceeding.
#2 – Carefully Inspect MAF Wiring
Begin by carefully inspecting the wiring associated with your vehicle’s MAF circuit. Check for signs of pinched, frayed, or otherwise damaged wires. Also, evaluate the condition of all circuit connectors. Rectify any damage before proceeding.
#3 – Inspect Vacuum System
Next, evaluate your vehicle’s vacuum system for any apparent leaks. Carefully check for intake leaks, or any dry rotted, cracked, or missing vacuum lines. Any deficiencies of this type should be repaired immediately.
#4 – Clean MAF Sensor
You will now clean your vehicle’s MAF sensor, using only approved cleaning solutions, and a soft nylon brush or similar utensil. Make sure that all oil fouling is removed in its entirety.
#5 – Evaluate O2 Sensor/Baro Sensor Data
Many vehicles utilize data supplied by all onboard oxygen sensors and barometric pressure sensors to rationalize feedback from the MAF sensor. With the use of an automotive scan tool, make sure that all data presented by these sensors falls within the range specified by your vehicle’s manufacturer.
#6 – Check MAF Voltage/Ground/Signal
You will now verify all input voltage and ground feeds, in accordance with manufacturer-specific service manual. If correct voltage and ground values are not present at the MAF sensor, troubleshoot the affected circuit as necessary.
If both supply voltage and ground are within the specified range, but output readings remain high when back-probed at the sensor itself, MAF sensor replacement will be necessary.
- P0480 Code (Symptoms, Causes, and How to Fix) - Apr 19, 2024
- Car Temperature Gauge Stopped Working? (Here’s Why) - Apr 15, 2024
- Ignition Coil vs Coil Pack (What’s the Difference?) - Apr 8, 2024
