P0110 Code (Symptoms, Causes, and How to Fix)
Today’s sophisticated engines rely on air temperature sensor data for intake calculations. Faulty readings from this critical sensor disrupt the air-fuel ratio, ignition timing, emissions and performance. When the intake air temperature circuit malfunctions, a P0110 code will present itself.
Keep reading to learn what exactly triggers code P0110, how severe it is, and what steps you should take to correctly resolve the issue.
What Does Code P0110 Mean?
Diagnostic trouble code P0110 is indicative of an operational fault within an engine’s intake air temperature circuit. A fault of this type prevents an engine’s ECM/PCM from acquiring valuable data utilized to determine an engine’s fuel trims.
However, to fully understand the gravity of DTC P0110, one must first familiarize themselves with the value provided by intake air temperature readings.
A vehicle’s intake air temperature sensor assists in determining variances in oxygen density. As a general rule, cooler air is more oxygen dense than warmer air. As a result, any discrepancy in intake air temperature can directly affect the combustibility of air introduced into an engine’s combination chambers. An engine’s ECM/PCM adapts to these variances by modifying relative fuel trims in real time.
In the case of DTC P110, an engine’s ECM/PCM is unable to obtain reliable readings from its corresponding intake air temperature circuit. As a result, engine efficiency suffers, as a wealth of critical data is excluded from a number of critical calculations.
Related: P0113 Code, P0480 Code
Symptoms of Code P0110

Diagnostic trouble code P0110 is often accompanied by a number of additional symptoms, many of which vary substantially in severity. Recognizing each of these symptoms often proves invaluable when attempting to diagnose and rectify the issue at hand.
The following are several of the most common symptoms associated with diagnostic trouble code P0110.
- Illuminated check engine light
- Erratic idle
- Hesitation under load
- Rich-smelling exhaust
- Backfiring
- Increased fuel consumption
Causes of Code P0110

Diagnostic fault code P0110 can be caused by a number of different underlying conditions. Understanding these numerous possibilities often serves as the difference between excessive downtime, and expedited repair.
The following are several of the most common causes of diagnostic fault code P0110.
- Bad intake air temperature sensor
- Compromised air intake temperature sensor wiring
- Damaged or corroded air temperature sensor plug
- Faulty powertrain control module (PCM)
Is Code P0110 Serious?
Diagnostic trouble code P0110 is generally considered to be of moderate severity. This is due primarily to the fact that this condition tends to have relatively detrimental effects on a vehicle’s overall drivability.
Poor idle and sub-par performance can both be attributed to faults within the air temperature sensor circuit, as can frequent backfiring.
Additionally, P0110-related faults can prove extra burdensome upon those living in states with regularly mandated emissions testing. This stems from the effects that this condition can have upon an engine’s fuel trims, as a vehicle’s PCM/ECM attempts to make up for the irrational data that it is receiving from this compromised circuit.
In any event, the root cause of diagnostic trouble code P0110 should be thoroughly diagnosed and repaired as soon as possible. Doing so prevents excess hardship, and eliminates much concern over the prospect of secondary issues.
If you don’t feel confident performing these repairs yourself, call a qualified auto repair shop or dealership at your earliest convenience.
How to Fix Code P0110
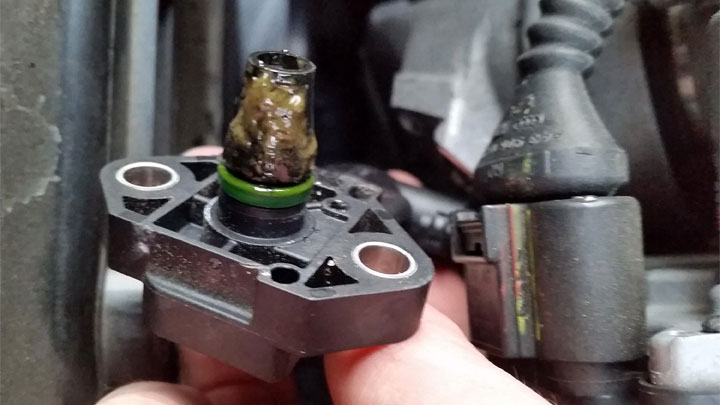

The following steps will assist you in diagnosing and repairing the root cause of your vehicle’s P0110 diagnostic fault code. As always, you should consult factory-specific service literature for your particular vehicle before attempting any such repairs.
#1 – Check For Additional DTCs
Before beginning the diagnostic process, carefully check for the presence of additional trouble codes, with the use of a quality scan tool. Any such codes should be thoroughly diagnosed and remedied before proceeding.
#2 – Inspect All Sensor Wiring
Begin by carefully inspecting all wiring associated with your engine’s intake air temperature sensor. Look for obvious signs of damage, such as skinned or pinched spots. Any damage of this type should be corrected before proceeding.
Additionally, one should also inspect the condition of their vehicle’s intake air temperature sensor connector.
#3 – Check For Proper Voltage/Ground
With the help of a factory-specific service manual for your vehicle, check to see if the supply voltage for your engine’s intake air temperature sensor is within specification. Additionally, verify that a satisfactory ground is provided to the circuit. Both of these values can be checked while back-probing the sensor connector with a multimeter.
#4 – Locate Circuit Instability
If the testing described in step #3 revealed a lack of supply voltage or ground, one must locate the source of this issue. This can be done by checking various parts of the circuit, while consulting a detailed wiring diagram. This condition must be rectified before proceeding.
#5 – Replace Sensor If Necessary
If testing conducted in step #3 failed to identify any notable issues, chances are good that your engine’s intake air temperature sensor has been compromised. This, in turn, will necessitate sensor replacement in order to remedy the issue at hand.
- P0480 Code (Symptoms, Causes, and How to Fix) - Apr 19, 2024
- Car Temperature Gauge Stopped Working? (Here’s Why) - Apr 15, 2024
- Ignition Coil vs Coil Pack (What’s the Difference?) - Apr 8, 2024
