Ignition Coil vs Coil Pack (What’s the Difference?)
Not all spark-ignition systems are the same from one engine to the next. This often causes significant confusion, especially when differentiating between ignition coils and coil packs.
Read on to learn about the multiple differences between these two ignition system components, and much more.
See Also: Timing Belt vs Timing Chain Comparison
Purpose
Though coil packs and ignition coils both play a significant role in delivering spark to an engine’s spark plugs, the manner in which each accomplishes this differs slightly.
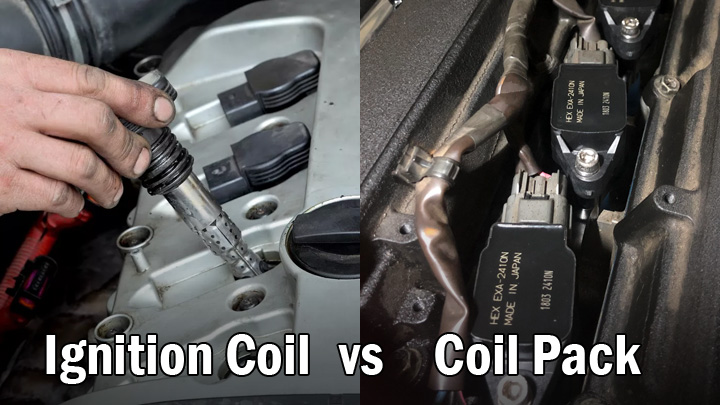
Ignition Coil
An ignition coil delivers stored energy to an engine’s distributor, via a specialized feed wire. This energy is then directed to the spark plugs found in each respective cylinder through distributor cap/rotor button interaction, and spark plug wire energization.
Coil Pack
Coil packs are commonly used on distributorless engines and are affixed to each spark plug in a direct or semi-direct fashion. Coil packs are energized in a timed manner, by a vehicle’s Engine Control Module or injector driver module.
Location
The standard location of an engine’s coil packs or ignition coil can differ significantly from one application to the next. This is due primarily to the way in which each operates.
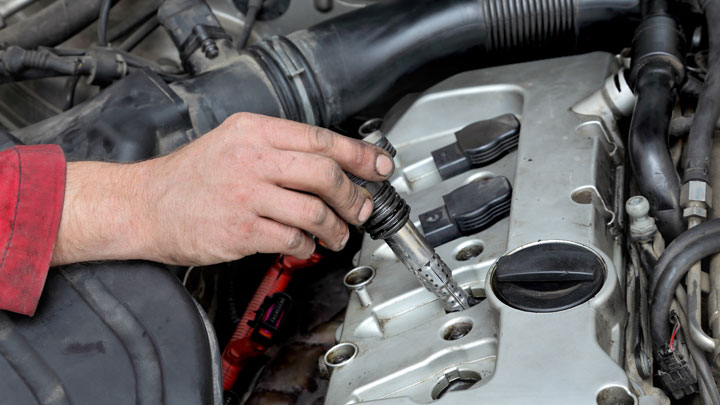

Ignition Coil
Generally, an engine’s ignition coil is mounted along one side of the block or the other. Perhaps the easiest way to locate an engine’s ignition coil is by tracing a distributor’s center wire or electrode back to its originating point at the ignition coil.
Coil Pack
An engine’s coil packs are typically mounted directly atop each cylinder’s spark plugs or alternatively, can be found affixed to the valve covers of each respective cylinder bank. In most cases, coil packs are easily located within the engine bay.
Construction
One of the most significant differences between ignition coils and coil packs comes in the form of their design. This difference stems from the parallel difference in the way that each component operates.
Ignition Coil

Typical ignition coils are of a cylindrical or “can” style design, featuring positive and negative studs, as well as a defined discharge terminal. Alternatively, later ignition coils tended to take on a squared-off appearance, often featuring both positive and negative leads within a single harness plug.
Coil Pack
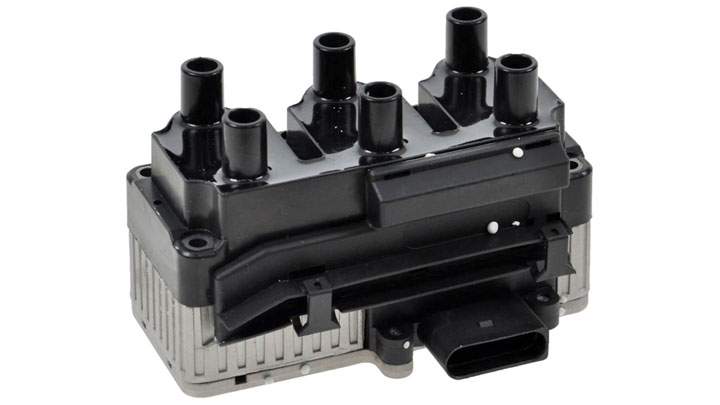

Coil packs are readily identified by their unique appearance. The typical coil pack generally features a moderately-sized coil, affixed to an integrated spark plug boot.
The lower portion of this assembly is almost always obscured from view when mounted to a vehicle’s engine, as the booted portion of the coil pack rests within a cylinder’s spark plug hole.
Reliability
While both ignition coils and coil packs tend to be relatively heavy duty, they are each prone to their own degree of reliability issues (especially as they age).
Ignition Coils
Ignition coils tend to exhibit lengthy service lives, ranging from 80,000-120,000 miles. Components of this type are most prone to experiencing failure when they encounter excess resistance, such as that which is often generated by aging or frail coil-to-distributor cables. Using an OBD2 scanner, a trouble code such as P0351 may signify a coil malfunction.
Coil Pack
Coil packs also tend to be relatively sturdy, typically lasting for 60,000-100,000 miles. However, coil packs are susceptible to arcing or grounding to other metallic surfaces under certain circumstances. This has proven especially true of coil-on-plug (COP) style coil packs.
Compatibility and Tunability
The selection of replacement ignition coils and coil packs should be handled carefully, as there are a number of special considerations that one should keep in mind when making such decisions.
Ignition Coils
Ignition coils are rated by the primary resistance within their windings and should be matched to the general requirements of the ignition system as a whole.
While performance coils are offered for use in high-output conditions, the use of an underpowered coil will lead to weak spark and poor engine performance.
Coil Pack
Coil packs are also generally purchased on an application-specific basis, due to their need to interface with a vehicle’s control modules.
If an engine is to be tuned, the purchase of performance coil packs might be a wise investment, as inadequately rated coil packs can fail rapidly when spark timing or feed voltage/amperage is modified.
Cost
There is a noteworthy difference in the cost associated with the purchase of an ignition coil and coil packs. This is due primarily to the somewhat more advanced design of the latter.
Ignition Coil
OE equivalent replacement ignition coils can be purchased at relatively reasonable prices, generally ranging between $40-$120. Additionally, only one ignition coil is required to repair an ignition system issue relating to engines of this design. On the contrary, since coil packs are cylinder-specific, more than one might be required under certain circumstances.
Coil Pack
Coil packs can be quite pricey to purchase when compared to the purchase of a single ignition coil. Though the price of coil-packs often varies from one make and model of vehicle to the next, one can generally expect to pay between $60-$180 for one unit. This price can jump astronomically if the replacement of multiple coil packs is required.
Replacement Difficulty
In most applications, the replacement of an ignition coil or coil pack is a relatively simple task to complete. Therefore, labor costs associated with such replacement are often relatively low.
Ignition Coil
The removal of a failed ignition coil often involves disconnecting 2 feed wires and a discharge cable before removal from a bracketed or clamped apparatus can be completed. Installation is largely conducted in reverse order of the above-described removal process.
In many cases, the most difficult task associated with the replacement of a defective ignition coil involves accessing the coil itself around other components in the engine bay.
Coil Pack
Coil pack replacement tends to be rather straightforward and simple to complete. Removal of the coil pack in question typically involves disconnecting one electrical plug and removing one-two hold-down screws, before twisting and pulling upward on the affected assembly.
Installation is achieved by following these steps in reverse order. Luckily, most coil packs are readily accessible for removal.
Comparison of Advantages/Disadvantages
Ignition Coil Pros
- Longer service life (80k-120k miles)
- Lower replacement cost ($40-$120)
- Only one coil required for repair
Ignition Coil Cons
- Requires a distributor system
- Less efficient spark delivery
- Access for replacement can be difficult
Coil Pack Pros
- Higher Quality spark and consistency
- Improved engine power and fuel efficiency
- Direct connection minimizes voltage leaks
- Easily accessible for replacement
Coil Pack Cons
- Shorter service life (60k-100k miles)
- Higher replacement cost ($60-$180 per unit)
- Multiple coil packs may need replacement
- Susceptible to arcing or grounding issues
- 5 Symptoms of an EVAP Leak (and Repair Cost) - Apr 27, 2024
- P0480 Code (Symptoms, Causes, and How to Fix) - Apr 19, 2024
- Car Temperature Gauge Stopped Working? (Here’s Why) - Apr 15, 2024
