P1682 Code (Symptoms, Causes, and How to Fix)
It seems as if each brand of vehicle found on the market today is prone to its own specific failures. These failures are manufacturer-specific enough that many such issues are presented with a fault code all their own.
This is the case with diagnostic fault code P1682 (ignition circuit issue), which is assigned primarily to vehicles under the General Motors umbrella (Chevrolet, GMC, Cadillac, Buick, and others).
Keep reading to learn more about DTC P1682, how to fix it, and whether you can continue driving until it gets resolved.

What Does Code P1682 Mean?
Diagnostic fault code P1682 is indicative of an imbalance in voltage between an ignition switch’s #1 & #2 circuits. This imbalance can wreak havoc on a vehicle’s electrical system if left unchecked, and can even lead to such issues as engine stalling, and/or starting-related issues.
However, to better understand this principle, one must first understand the inner workings of a GM ignition switch.
In the current era, GM uses an ignition switch that features 2 distinct positive ignition switch feeds, the first of which powers the ECM and throttle actuator. Meanwhile, the second of these positive feeds delivers power to the run/crank circuit, and all associated relays.
The difference between the positive energy found on each of these two circuit legs is monitored at all times.
Whenever voltage attributed to the second leg of the ignition circuit differentiates from that which is observed on circuit leg #1 by more than anticipated, diagnostic fault code P1682 is logged. As a result, the affected vehicle’s check engine light is logged.
As long as this voltage imbalance continues to be recorded, diagnostic fault code P1682 will remain active, and the above-mentioned check engine like will continue to illuminate.
More often than not, diagnostic fault code P1682 can be attributed to a faulty ignition switch, or compromised wiring related to this particular switch. Consequent testing of the previously mentioned components often yields a satisfactory diagnosis.
Luckily, a vehicle’s ignition switch tends to be relatively cost-efficient to replace, and the parts required for such repairs are readily available at almost every parts house.
Symptoms of Code P1682

Diagnostic fault code P1682 is often accompanied by a range of secondary symptoms, some of which tend to be far more concerning than others. Identifying these symptoms is the first step to take to identifying the issue, and making a timely repair.
These are the most frequently reported symptoms associated with DTC P1682.
- Engine stalling
- Unexplainable battery discharge
- Illuminated check engine light
- Starting failures
- Dim headlights
- Repeated blowing of fuses
Causes of Code P1682
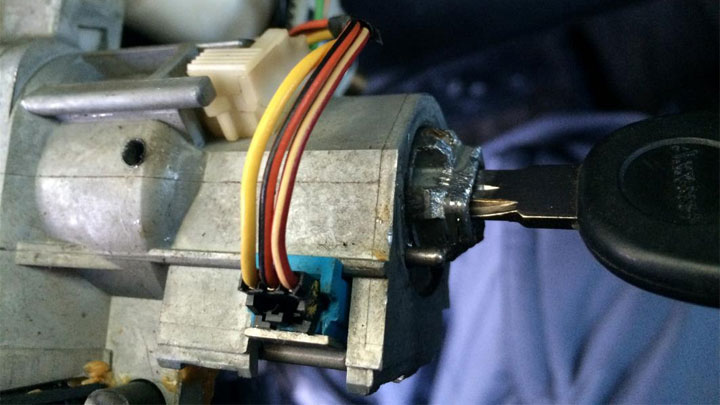
A P1682 code can be caused by several underlying issues, some of which are more challenging to identify than others. Technicians and DIY enthusiasts who are familiar with the potential causes will have the best chance at a quick diagnosis and repair.
Here are some of the most common causes of DTC P1682.
- Failed ignition switch
- Faulty ignition switch harness
- Loose circuit electrical connections
- Compromised ECM/PCM
Is Code P1682 Serious?
Diagnostic fault code P1682 is generally considered to be moderately serious in nature, due primarily to the driveability-related concerns connected to this particular issue. You can find yourself stranded in light of a code P1682, and much like any mechanical/electrical issue, the underlying cause of this trouble code is only likely to worsen with time.
Some of the most concerning symptoms related to diagnostic fault code P1682 are those that have to do with engine stalling. In the most severe of cases, a vehicle’s engine can simply shut off while driving, much as if you had turned off the ignition yourself.
Another valid concern related to fault P1682 is connected to starting related issues. As symptoms worsen, you can find yourself stuck, without the ability to start your vehicle’s engine.
In any event, the root cause of a vehicle’s P1682 fault code should be diagnosed and repaired as soon as possible. Doing so ensures that you or your loved ones are not left stranded roadside. If you don’t feel comfortable tackling this type of repair on your own, an appointment should be scheduled with a trusted service center as soon as possible.
How to Fix Code P1682

Follow the steps below to help diagnose and repair the root cause of a vehicle’s P1682 fault code. Be sure to consult factory-specific service literature for your particular model of vehicle so you have the most accurate information available.
#1 – Check For Additional DTCs
Before beginning the diagnostic process, check for the presence of additional diagnostic fault codes. Any such codes that are found should be thoroughly diagnosed before proceeding. Any high-priority faults should be fixed immediately, as they could serve as the underlying cause of the problem.
#2 – Inspect Wiring
Begin by carefully inspecting the under-dash wiring to your vehicle’s ignition switch. All wiring should be intact, and free of corrosion or rub marks. It is also important to make sure that the individual connector related to the affected vehicle’s ignition switch is secured as it should be.
#3 – Trace Wiring To ECM
Next, trace all related wiring from the vehicle’s ignition switch to the vehicle’s ECM/PCM. Check For signs of chafing or pinching. Rectify any abnormal conditions that are present, by replacing the compromised harness as a whole.
#4 – Pin-Out Wiring Harness
If no issues have presented themselves to this point, the affected vehicle’s wiring harness will require “pin-out” testing, in accordance with factory-mandated service protocols. Conduct this testing in the most thorough manner possible, as it will isolate the issue at hand to the ignition switch, or the vehicle’s ECM/PCM.
#5 – Replace Defective Components as Necessary
The above-mentioned testing should have revealed one or more defective components. In most cases, the component in question will be the affected vehicle’s ignition switch.
Occasionally, this failure might indeed be related to the vehicle’s ECM/PCM itself. When this occurs, subsequent reflashing of the control module in question is often required to re-establish connectivity with various other modules.
- P0480 Code (Symptoms, Causes, and How to Fix) - Apr 19, 2024
- Car Temperature Gauge Stopped Working? (Here’s Why) - Apr 15, 2024
- Ignition Coil vs Coil Pack (What’s the Difference?) - Apr 8, 2024
