Toyota RCTA and BSM Malfunctions (Causes and Troubleshooting Advice)
Have you recently been greeted by an “RCTA Unavailable” or “BSM Off” message on the dash of your Toyota, Lexus, or other brand that uses this naming convention?
These alerts indicate issues with your vehicle’s Rear Cross-Traffic Alert and Blind Spot Monitoring systems.
Keep reading to learn common causes behind these malfunctions, practical troubleshooting advice, and whether it’s safe to continue driving.
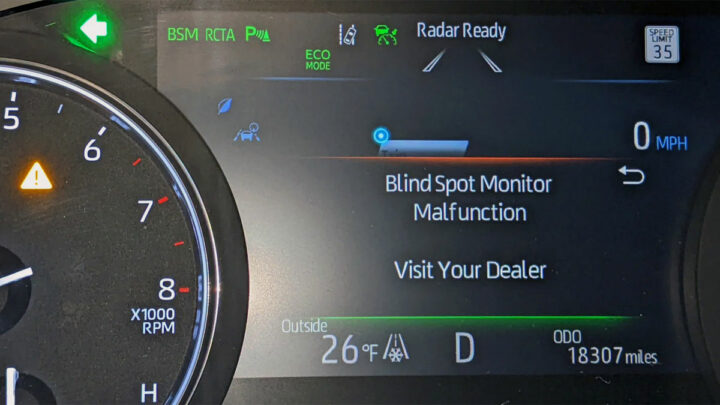
What is Toyota RCTA?
“RTCA” stands for Rear Cross-Traffic Alert, and is a phrase coined primarily by Toyota.
The system is designed to monitor the approach of cross-traffic in relation to the rear of a vehicle, primarily when the vehicle in question is involved in a backing maneuver. Detection of this type is afforded through the use of specialized rear-facing radar probes.
What is Toyota BSM?
“BSM” stands for Blind Spot Monitoring, and generally serves as the nomenclature for such technology industry-wide.
Toyota BSM is a system that is intended to provide critical monitoring within a vehicle’s blind spot, to a greater extent than what traditionally would be afforded through the use of mirrors alone.
Like the aforementioned RCTA system, BSM systems utilize specialized radar probes to acquire critical feedback used in the detection of overtaking traffic.

What Causes a “Rear Cross-Traffic Alert Unavailable” or “RCTA Off” Message to Appear?
RCTA-related fault messages can be logged for a number of reasons. However, the most common of these reasons relates to dirty or obstructed sensors (radar probes).
These messages are often displayed when ice or frost covers the probes in question, or when a vehicle becomes saturated in dirt or mud. In such cases, the root cause of such failures is purely environmental and largely temporary.
Other causes for RCTA faults can include radar probe damage or failure, wiring-related issues, or module interface degradation.
In many cases, such issues are best diagnosed with the assistance of a trained professional, due to the complexities of the system itself. Professional diagnostics can also prevent costs accrued from changing parts that are, in fact, not faulty.
See Also: What Does “Park Assist Blocked” Mean?
What Causes a “Blind Spot Monitor Unavailable” or “BSM Off” Message to Appear?
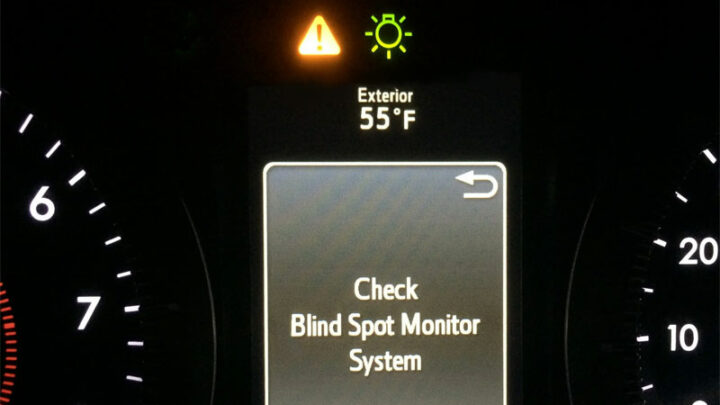
BSM faults are typically attributed to many of the same underlying issues as those that commonly afflict RCTA systems, the number one of which tends to center around dirty, fouled, or obstructed sensors (radar probes).
Again, many of these issues can simply be resolved by cleaning the affected sensors/probes. In the case of ice or frost fouling, you might be required to carefully defrost these sensors, or otherwise wait for temperatures to rise above freezing.
Also of note, is the fact that electrical failure of these components can happen as they begin to age, thereby necessitating replacement.
But aside from this, damage from debris strikes and collisions are also potential causes of BSM system interoperability. Therefore, thorough visual inspection is key when attempting to pinpoint the root cause of any BSM-related issue.
Is It Safe to Continue Driving?
Yes, it is safe to continue driving in the midst of RTCA and/or BSM issues. Faults related to these systems generally disable their functionality as a whole.
Because of that, a fault in this regard will lead to a vehicle operating in virtually the exact same manner as any vehicle would have prior to the rise of the technology.
It is, however, worth noting that you should be careful to take extra precautions when driving a vehicle with a malfunctioning or inoperative RCTA/BSM system. This is especially true if you’ve become quite accustomed to driving cars equipped with such safety features, as a driver can easily become over-reliant upon the technology of this type.
Troubleshooting RCTA and BSM Issues
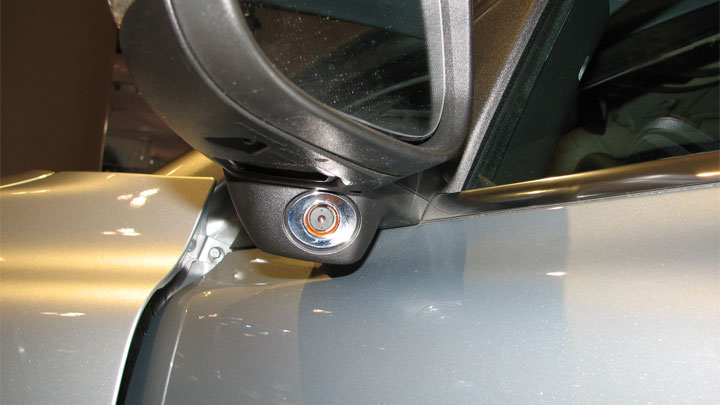

The most efficient way to troubleshoot RCTA and BSM-related issues typically involves employing the use of a quality OBD-II scan tool.
A scanner of this type will be capable of reading any active or stored faults related to the BSM module. This should allow you to hone in on the root cause of the failure, and make efficient repairs.
If a radar probe fault or feedback fault is logged, you should focus the bulk of your attention on making sure that your vehicle’s radar probes/sensors are securely mounted and that all connections are viable, and without obvious issues.
While conducting these inspections, it also makes sense to check each individual sensor to make sure it is clean and not obstructed in any way.
Finally, it’s also important to check the health of your vehicle’s battery, as well as that of its starting and charging system. Even minor voltage abnormalities are known to wreak havoc on BSM-related systems, causing difficult to pinpoint feedback and connectivity issues.
In these instances, nothing more than a failing battery can be a cause for major headaches.
When to Visit the Dealer
In many cases, the diagnosis and repair of RCTA and/or BSM-related issues is best left to industry professionals if you’ve confirmed the all sensors are clean with no obvious obstructions.
This is due to the fact that these types of systems tend to be relatively complex in nature, and can require the use of specialty tooling to repair. If ever in doubt, especially when the cause of such issues does not appear blatantly obvious, professional assistance is recommended.
How to Manually Turn Off RCTA or BSM

While rear cross-traffic and blind-spot monitoring technology may prove the be helpful most of the time, there may be situations like when towing, driving off-road, or in tight, crowded areas where you may want to temporarily disable this technology to avoid unnecessary warnings or distractions.
The manner in which RTCA and/or BSM systems are manually disabled generally differs from one make and model of vehicle to the next. However, in most cases, this is accomplished through accessing a selectable instrument cluster based menu, such as the Multi-Information Display on Toyota and Lexus models.
Simple menu tabs allow such systems to be toggled into the “off” position. Alternatively, some vehicles feature a basic toggle or button style switch that is used to turn the systems on or off.
Do These Systems Use the Same Sensors?
In most instances, today’s vehicles do in fact use the same sensors to facilitate the operation of their RCTA and BSM systems.
All systems of this nature utilize proprietary radar-type sensors that supply vital feedback to various control modules. The difference between RCTA and BSM systems comes down to the manner in which this feedback is interpreted.
- P0480 Code (Symptoms, Causes, and How to Fix) - Apr 19, 2024
- Car Temperature Gauge Stopped Working? (Here’s Why) - Apr 15, 2024
- Ignition Coil vs Coil Pack (What’s the Difference?) - Apr 8, 2024
