P0344 Code (Symptoms, Causes, and How to Fix)
That dreaded check engine light strikes fear in the hearts of drivers everywhere. But don’t panic when a P0344 code is the result. While it sounds ominous, this trouble code is often caused by minor issues.
Let’s explore the meaning and common culprits behind code P0344 and how to get your engine running smoothly again without breaking the bank.

What Does Code P0344 Mean?
Diagnostic fault code P0344 alludes to a detected lack of camshaft position sensor feedback stability. Simply put, the affected vehicle’s ECM/PCM has determined feedback from its corresponding camshaft position sensor to be erratic or Intermittent.
This, in turn, compromises the ECM/PCM’S ability to utilize the anticipated feedback from this sensor to formulate further engine strategy.
To better understand the complexities of diagnostic fault code P0344, it’s best to first familiarize yourself with the role of the camshaft position sensor in modern engine operation.
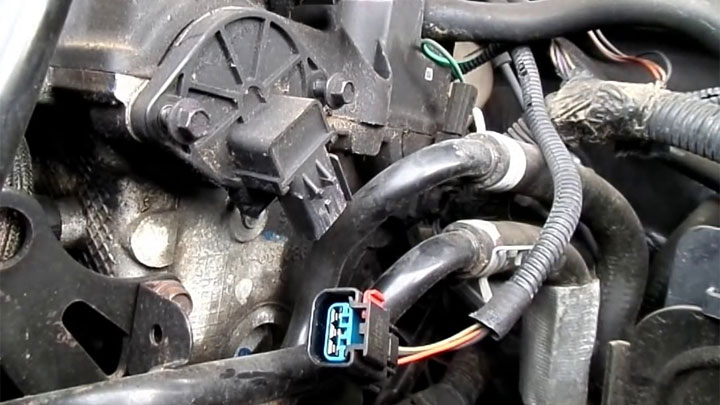

Today’s electrically-monitored engines rely heavily upon input from a number of sensors to formulate engine operational strategy as a whole few of these sensors are as vital as those relating to engine timing, with the camshaft position sensor being the most accurate of these sensors.
Without valid feedback from an engine’s camshaft position sensor, a vehicle’s ECM/PCM is unable to accurately determine proper fuel injection timing, as no top-end timing measurements are retained or logged. Furthermore, other engine functions, such as variable valve timing, are also negated.
In the case of DTC P0344, a vehicle’s operating software is momentarily losing connection with the engine’s camshaft position sensor, thereby failing to execute several timing-sensitive functions, as it otherwise should.
As a result, a number of severe driveability-related symptoms often arise, including stalling/starting difficulties.
Symptoms of Code P0344
Diagnostic fault code P0344 is often accompanied by a number of secondary symptoms, some of which tend to be quite troubling in nature. Those who are familiar with such symptoms will be at an advantage when it comes to diagnosing and repairing problem.
The following are several of the most common symptoms associated with DTC P0344.
Causes of Code P0344
Diagnostic fault code P0344 can be caused by one of several underlying symptoms, some of which often prove more difficult to pinpoint than others. As in any case, understanding the potential causes of such an issue can make all the difference when attempting to make a timely repair.
The following are several of the most common causes of DTC P0344:
- Open/short in cam sensor power supply circuit
- Open/short in cam sensor ground supply circuit
- Open/short in cam sensor feedback circuit
- Faulty camshaft position sensor
- Damaged camshaft tone ring
Is Code P0344 Serious?

Generally speaking, diagnostic fault code P0344 is regarded by most as being rather serious in nature. This, in large part, is due to the numerous driveability-related symptoms that often accompany faults of this nature.
Any issue that could potentially leave you and your vehicle stranded, is not an issue to take lightly or to overlook.
Intermittent hesitation and stalling are both potential symptoms of an active P0344 diagnostic fault code. Continuing to drive with your vehicle in such shape can pose a serious risk to person and property, should your vehicle unexpectedly stall in the flow of traffic (especially at highway speeds).
In any event, the cause of a vehicle’s P0344 diagnostic fault code should be thoroughly diagnosed and repaired at the first available opportunity. This is the only reliable way to make sure your car runs safely and efficiently.
If you don’t feel able to make the repairs yourself, schedule an appointment with a trusted auto repair shop or dealership at your earliest convenience.
How to Fix Code P0344
The following steps can be used to assist you in diagnosing and repairing the root cause of your vehicle’s P0344 fault code. As always, a factory-specific manual (like Haynes, Chilton, or online source) should be consulted for your particular model of vehicle before attempting any such repairs.
#1 – Check For Additional DTCs
Before beginning the diagnostic process, it’s important to check for the presence of any additional DTCs. Any DTCs that are found should be thoroughly diagnosed before proceeding.
#2 – Inspect Camshaft Position Sensor
One should start by carefully inspecting their engine’s camshaft position sensor for signs of undue stress or damage. Any evident damage to the camshaft position sensor itself will necessitate replacement.
Likewise, any damage to the sensor’s electrical harness should be repaired or replaced immediately.
#3 – Analyze Freeze Frame Data
Next, view all freeze frame data associated with the storage of DTC P0344. Determine the number of times that camshaft sensor feedback has been interrupted, as well as the frequency with which such failures occur.
Similarly, you should attempt to determine any common denominators, in terms of recorded data, that might assist in isolating the cause of this fault.
#4 – Determine Sensor Type
At this point, further diagnosis will require you to identify the type of camshaft sensor your vehicle is equipped with.
If your vehicle’s camshaft position sensor is fitted with 2 wires, it is of a magnetic pickup style. If this sensor has 3 wires, it is a Hall Effect sensor.
#5 – Testing Magnetic Pickup Sensors
If your vehicle’s camshaft position sensor is of a magnetic pickup configuration, resistance should be checked across both terminals of this sensor itself with it disconnected. This resistance reading should be compared to figures specified by your vehicle’s manufacturer.
Additionally, these two terminals should also be probed while having an assistant attempt to crank the engine in question, with your meter set to A/C volts. Again, this reading should be compared to manufacturer specifications, though .5V AC is generally satisfactory.
#6 – Test Hall Effect Sensor
If your vehicle’s camshaft position sensor is of the Hall Effect style, a multimeter should be used to test the corresponding harness to ensure that a satisfactory source of power (5V) and ground is present.
If both values are present to the sensor itself, live data derived from your OBD2 scan tool should be consulted to verify that proper feedback is being supplied to the PCM.
- 5 Symptoms of an EVAP Leak (and Repair Cost) - Apr 27, 2024
- P0480 Code (Symptoms, Causes, and How to Fix) - Apr 19, 2024
- Car Temperature Gauge Stopped Working? (Here’s Why) - Apr 15, 2024
