Diesel Engine vs Gasoline Engine (Comparison)
Internal combustion engines have truly been a hallmark of 20th century invention and innovation. They have powered cars, trucks, aircraft, boats, and much more. These are machines that are the workhorse of the modern era, so it helps to know a bit about how they function, and what characterizes their operation.
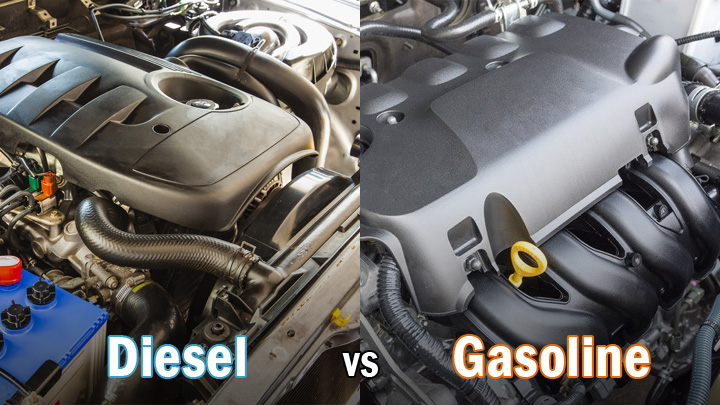
Though both rely on internal combustion, gasoline and diesel engines differ in key ways. Understanding these unique powerplants is essential knowledge for gearheads and everyday drivers alike.

See Also: Can Gas or Diesel Freeze in Extreme Cold Weather?
Gasoline vs Diesel (Fundamental Differences)
When it comes to the main similarity between gasoline and diesel engines, this is of course the fact that both engines utilize the principles of internal combustion for energy generation and basic propulsion.
They both work from the basic inputs of heat and pressure to drive an internal mechanical structure which transfers power to the axles and wheels that make a vehicle move.
When we address the differences with gasoline and diesel engines, one of the most obvious differences is the type of fuel being added to the vehicle. Diesel fuel is different than conventional unleaded gasoline, and these fuels are not compatible.
In other words, if a driver attempts to put diesel fuel in their conventional automobile, they will be calling a tow truck soon after.
Related: What Happens When You Put Gas in a Diesel Engine?
Mechanically speaking, the primary difference between gasoline and diesel engines is in the way the internal engine explosions are taking place. Within a typical gasoline engine’s combustion process, the fuel is going to be first mixed with air, then the mixture is compressed and ignition takes place via spark input from a spark plug.
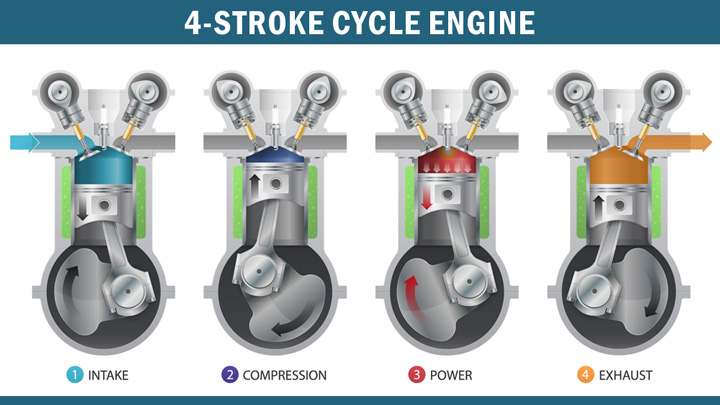
This basic model for combustion is different with diesels. The reason for this is because in a diesel engine, the incoming air is actually going to be compressed as the first step in the process. After the air is compressed first, then the diesel fuel will be injected afterwards.
Similarities Between Gasoline and Diesel Engines

#1 – Both Considered to be Internal Combustion Engines
Both gas and diesel engines are internal combustion engines, meaning that they use a combustion process to generate power. This process involves a mixture of air and fuel being ignited inside a cylinder, which then creates a pressure that forces the piston to move. The piston’s motion turns the crankshaft, generating power to the drivetrain.
#2 – Require Fuel and Air to Function
Each type of engine requires a mixture of fuel and air in order to operate. The fuel is combined with air, creating an explosive mixture which is then ignited inside the cylinder. This creates combustion and pressure, which pushes the piston down, generating power.
#3 – Use Pistons to Move the Air/Fuel Mixture to Generate Power
Pistons are an essential part of both gasoline and diesel engines. These pistons move up and down inside the cylinder walls, creating pressure when the fuel and air mixture is ignited. This pressure forces the piston down, turning the crankshaft and generating power.
Related: Gasoline vs Hybrid Cars
Other Comparisons
Fuel Efficiency
Diesel engines generally have higher fuel efficiency compared to gasoline engines due to their superior thermal efficiency and higher compression ratios.
On average, diesel engines can deliver 20-35% better fuel economy than gasoline engines. However, actual fuel efficiency depends on factors such as vehicle weight, aerodynamics, gearing, and driving conditions.
While diesel fuel contains more energy per gallon, it is also typically more expensive than gasoline. Recent advancements in gasoline engine technology have narrowed the fuel efficiency gap between the two engine types.
Maintenance Requirements

Diesel and gasoline engines have distinct maintenance requirements due to their different operating principles and design characteristics.
Diesel engines are known for their robustness and longevity, partly because they do not require a spark ignition system. However, they need more complex fuel filtration to handle impurities in diesel fuel and may require more frequent air filter replacements due to the high volume of air needed for combustion.
Modern diesel engines also come with advanced emission control systems, such as Diesel Particulate Filters (DPF) and Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR), which require periodic maintenance.
Gasoline engines, have their own set of maintenance needs. The ignition system, which includes spark plugs and wires, requires regular replacement as these components wear out over time. Gasoline engines typically need oil changes every 3,000 to 5,000 miles, though newer models often have longer intervals (7,500 to 10,000 miles).
Maintaining the cooling system is important to prevent overheating, and the fuel system, including fuel filters and injectors, may require periodic cleaning or servicing.
Despite their differences, both diesel and gasoline engines share some common maintenance tasks. These include regular oil changes (with oil type and interval varying by engine type), maintaining proper coolant levels and condition, inspecting and replacing belts and hoses, battery maintenance, air filter replacement, tire rotation, and alignments among others.
Longevity and Durability

Both diesel and gasoline engines have their strengths and weaknesses when it comes to longevity/durability. Diesel engines are known for their heavy duty construction and long-lasting performance. They are built to withstand the high compression ratios necessary for diesel combustion, which results in stronger engine components.
This durability makes diesel engines a popular choice for heavy-duty applications, such as trucks, buses, and construction equipment. With proper maintenance, a diesel engine can easily last for 500,000 miles or more.
Gasoline engines, have a reputation for being less durable than their diesel counterparts. However, advancements in technology and manufacturing processes have significantly improved the longevity of gasoline engines in recent years.
Modern gasoline engines feature more durable materials, better cooling systems, and improved lubrication, which all contribute to longer engine life. When properly maintained, a gasoline engine can last for 200,000 miles or more.
One factor that can impact the longevity of both diesel and gasoline engines is the quality of fuel used. Diesel engines are particularly sensitive to fuel quality, as poor-quality diesel fuel can cause damage to the fuel injection system and lead to reduced engine life.
Gasoline engines are less sensitive to fuel quality, but using low-quality or contaminated gasoline can still cause problems over time.
Ultimately, the longevity and durability of a diesel or gasoline engine depend on a combination of factors, including the quality of the engine design, the materials used, and the care taken by the owner to maintain the engine over time.
Applications
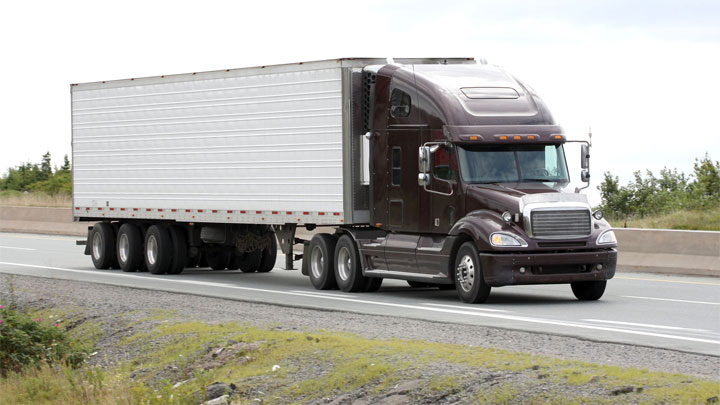

One of the predominant uses of diesel engines in the world today is in the transit of raw materials and goods. Most of the worlds overland shipping is actually carried out by the use of large scale diesel engine eighteen-wheel style trucks.
Related: Why Do Some Trucks Have Spikes on Their Wheels?
These kinds of commercial trucks carry huge amounts of cargo and goods at a time, and there are many different trucks all operating at the same time on the world’s roadways.
Conventional gasoline engines on the other hand are much more oriented for consumer transit and travel, as they are typically outfitted in most consumer cars, trucks, and SUV’s with the exception of a view diesel makes and models here and there.
Future Trends of Diesel and Gasoline Engines
The future of diesel and gasoline engines is an exciting and rapidly changing landscape, influenced by environmental concerns, government regulations, and new technologies.
One of the most significant trends is the growing use of electrification and hybrid technology. By combining the power of diesel and gasoline engines with the clean energy of electric motors, automakers are creating a new generation of vehicles that offer the best of both worlds.
From mild-hybrid systems that provide a small electric boost to plug-in hybrids that can run on electricity alone for short distances, the future of the internal combustion engine is becoming more and more connected with the rise of electrification.
But the evolution of diesel and gasoline engines goes beyond just hybridization. New technologies, such as direct fuel injection and variable valve timing, are improving efficiency and performance.
Innovations in emission control, like advanced diesel particulate filters and catalytic converters, are helping to reduce the environmental impact of these engines. Additionally, the use of alternative fuels, such as biodiesel and ethanol, is providing a more eco-friendly option without the need for a complete redesign of existing engines.
Looking ahead, the impact of connected and self-driving vehicle technologies cannot be ignored. The growth of vehicle-to-vehicle communication and autonomous driving has the potential to change the way engines are used, optimizing driving patterns for maximum efficiency and reducing wear and tear.
Predictive maintenance, made possible by advanced sensors and data analysis, will help keep these engines running smoothly while minimizing downtime. However, the shift towards alternative power sources, such as fully electric and hydrogen fuel cell technologies, is a clear force shaping the future of transportation.
As infrastructure improves, costs go down, and consumer acceptance grows, the long-term future of diesel and gasoline engines remains uncertain. Nevertheless, for the near future, these tried-and-true engines will continue to evolve and adapt, playing a vital role in the complex world of transportation.
- Replace the Engine or Replace the Car? (11 Factors to Consider) - Apr 11, 2024
- Plastic Piece Dragging Under Your Car? (What It Is and What To Do) - Mar 21, 2024
- Timing Belt vs Timing Chain (What’s the Difference?) - Feb 27, 2024

I would like to know more about engine please help me understand more about Diesel engine four cylinder and six cylinder engine