P0050 Code (Symptoms, Causes, and How to Fix)
Oxygen sensors play a vital role in engine efficiency, monitoring exhaust to fine-tune fuel delivery. But to function properly, they must reach operating temperature via an internal heater circuit. When this heater fails, the sensor can’t provide accurate readings and code P0050 is triggered.
Read on to better understand the P0050 code, its causes, and how to accurately diagnose and fix the problem at hand.

What Does Code P0050 Mean?
Diagnostic fault code P0050 pertains to a defined issue within the heater control circuit of a vehicle’s bank 2, position 1 oxygen sensor. This circuit is responsible for ensuring that the oxygen sensor itself quickly heats to the necessary temperature for accurate detection.
Without the heater circuit intact and operating as it should, an O2 sensor’s accuracy is severely limited during the first several minutes of operation. To better grasp this principle, you need to first learn how an oxygen sensor in a car works.
Most vehicles are equipped with a minimum of 2 oxygen sensors, with engines of a “V” configuration featuring a total of 4 sensors. In either case, O2 sensors are positioned both upstream and downstream of a vehicle’s exhaust catalyst.
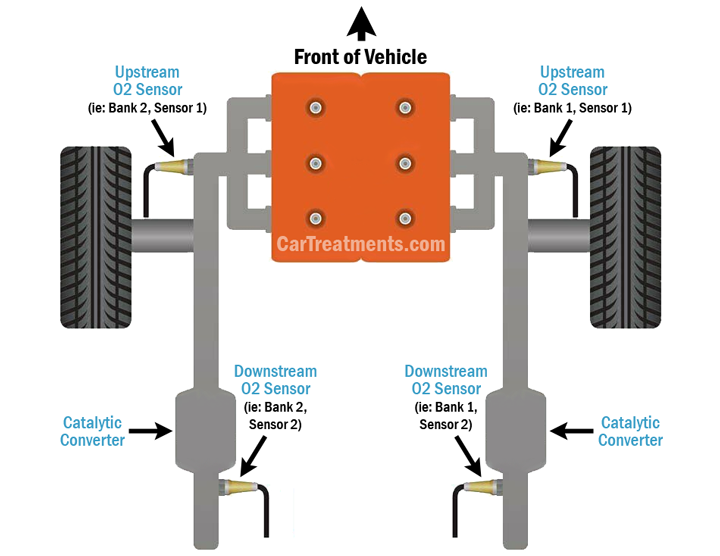
Each of a vehicle’s oxygen sensors works to detect oxygen levels in spent combustion gasses routed through a vehicle’s exhaust. This information is then directed to a vehicle’s PCM, where it is used to calculate necessary adjustments in fuel delivery. Additionally, values from upstream and downstream O2 sensors are compared to estimate catalyst efficiency.
For an oxygen sensor to accurately record the oxygen content of any exhaust gasses that it samples, it must operate at a temperature similar to that of the vehicle’s exhaust to which it is mounted. To make sure that this temperature is achieved, today’s O2 sensors are equipped with integrated heaters that rapidly warm them to sufficient temperatures at startup.
In the case of DTC P0050, an issue has been detected within the heater circuit of a vehicle’s pre-catalyst, bank 2 oxygen sensor. As a result, detection accuracy is compromised until suitable operating temperatures have been achieved through natural heating. This, in turn, can reduce a vehicle’s ability to monitor combustion and catalyst efficiency as a whole.
See Also: P0030, P0031, P0032, P0036, P0037, P0051
Symptoms of Code P0050
Diagnostic fault code P0050 is often associated with one or more secondary symptoms, some of which tend to be more noticeable than others. Recognizing these symptoms can prove invaluable when attempting to diagnose the issue at hand.
The following are several of the most common symptoms associated with DTC P0050.
- Illuminated check engine light
- Rough or irregular idle
- Reduced fuel economy
Causes of Code P0050

Diagnostic fault code P0050 can be caused by a number of underlying issues, some of which are more easily identified than others. Those who are familiar with these potential causes can often expedite the diagnostic and repair process as a whole.
The following are several of the most common causes of DTC P0050.
- Bank 2, sensor 1 O2 sensor failure
- Damaged O2 sensor wiring
- Corroded O2 sensor connection
- PCM failure
Is Code P0050 Serious?
Diagnostic fault code P0050 is generally considered to be of lower severity, but in the most severe of cases, this fault can cause a vehicle’s engine to run erratically, due to its potential impacts upon an engine’s applicable fuel trims. Additionally, the extended operation of an engine in this shape can cause undue stress on various internal components.
If you live in a state that requires mandated emissions testing, you should also be aware that the presence of an active DTC P0050 fault code, will often result in an automatic failure. This stems from the fact that a vehicle’s O2 sensors are considered pieces of essential emissions equipment.
In any event, the root cause of a vehicle’s P0050 diagnostic fault code should be thoroughly diagnosed and repaired as soon as possible. Doing so will restore a vehicle to peak performance, and prevent undue internal engine stress.
If you don’t feel confident doing these repairs yourself, you should schedule an appointment with a reliable service center as soon as possible.
How to Fix Code P0050

The following steps can be used to assist in diagnosing and repairing the root cause of your vehicle’s P0050 diagnostic fault code. As always, factory-specific service literature for your particular model of vehicle should be consulted before attempting any such repairs.
#1 – Check For Additional DTCs
Before beginning the diagnostic process, you should check for the presence of additional DTCs. Any such DTCs that are found should be thoroughly diagnosed before proceeding.
#2 – Inspect Affected O2 Sensor/Wiring
Begin by carefully inspecting the vehicle’s bank 2, sensor 1 oxygen sensor. Check for obvious signs of damage to the affected O2 sensor, and related wiring. Additionally, the connector for this sensor should be checked for signs of water intrusion or corrosion. Any obvious defects should be repaired before continuing.
#3 – Check For Voltage/Ground Delivery
If no visible defects have been found to this point, it will be necessary to check for the presence of power and ground at the affected O2 sensor’s connector.
If either of these are not present a thorough check of the power distribution circuit will be required. If both power and ground are being delivered as specified by the vehicle’s manufacturer, then the affected O2 will need to be replaced.
#4 – Test PCM
If the PCM itself is suspected of being faulty, subsequent testing per manufacturer recommendation will be required. You should never assume the PCM to be faulty, without full diagnostics being completed as the cost of PCM replacement is not cheap.
- P0480 Code (Symptoms, Causes, and How to Fix) - Apr 19, 2024
- Car Temperature Gauge Stopped Working? (Here’s Why) - Apr 15, 2024
- Ignition Coil vs Coil Pack (What’s the Difference?) - Apr 8, 2024
